Tables in Microsoft Words
Creating a Table
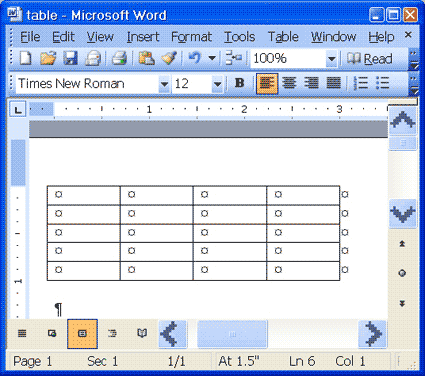
To create a four-column, five-row table:- Choose Table > Insert > Table from the menu. The Insert Table dialog box opens.
- Type 4 in the Number of Columns field.
- Type 5 in the Number of Rows field.
- Select Auto in the Column Width field. Selecting Auto allows Microsoft Word to determine the size of your column widths. Alternatively, you can enter the column width you desire.
- Click OK. Your table should look like the one shown here, with four columns and five rows.
Alternate Method -- Creating a Table by Using the Insert Table Icon
You can also create a table by clicking on the Insert Table icon on the Standard toolbar.- Click the Insert Table icon.

- Highlight the number of rows and columns you need. The maximum table size you can create by this method is a four-row by five-column table.
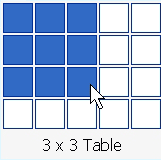
- Press Enter (or click) to create the table.
Moving Around a Table
Each block in a table is called a cell. Use the Tab key to move from cell to cell from left to right. Use Shift-Tab to move from cell to cell from right to left. The following exercise demonstrates.- Click in the first cell in the first column.
- Press the Tab key nine times. The cursor moves forward nine cells.
- Press Shift-Tab six times. The cursor moves backward six cells.
Entering Text into a Table
To enter text into a table, simply type as you normally would. Press Tab to move to the next cell. Enter the text shown below into your table.- Type Salesperson in the first cell in the first column. Press the Tab key.
- Type Dolls in the first cell in the second column. Press the Tab key.
- Continue until you have entered all of the text.
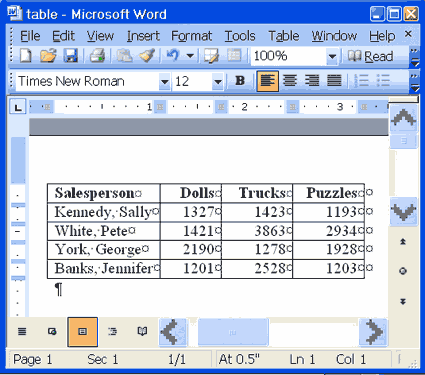
| Salesperson | Dolls | Trucks | Puzzles |
| Kennedy, Sally | 1327 | 1423 | 1193 |
| White, Pete | 1421 | 3863 | 2934 |
| York, George | 2190 | 1278 | 1928 |
| Banks, Jennifer | 1201 | 2528 | 1203 |
Selecting a Row and Bolding the Text
You learned about bolding in Lesson Three. In this exercise, you will select the first row of the table and bold all of the text on the row.- Click anywhere on the first row of your table.
- Choose Table > Select > Row from the menu.
- Press Ctrl-b to bold the row.
Right-Aligning Text
You learned about alignment in Lesson Five. In this exercise, you will right-align the second (Dolls), third (Trucks), and fourth (Puzzles) columns of the table you created.- You need to highlight "Dolls," "Trucks," and "Puzzles." Place the cursor before the "D" in "Dolls." Press the F8 key to anchor the cursor. Then press the right arrow key until you have highlighted "Dolls," "Trucks," and "Puzzles."
- Choose Table > Select > Column from the menu.
- Press Ctrl-r to right-align the cells.
Adding a New Row to the End of the Table
You can add additional rows to your table. The simplest way to add a new row is to move to the last column of the last row and press the Tab key. You can then type any additional text you need to add.- Move to the last column of the last row of your table.
- Press the Tab key.
- Type the text shown here.
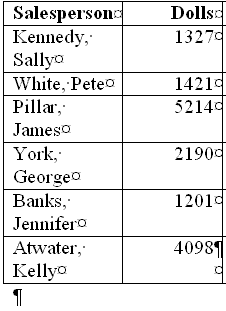
| Atwater, Kelly | 4098 | 3079 | 2067 |
Adding a Row Within the Table
You can add a new row anywhere in the table. The exercise that follows demonstrates.To add a row just above York, George:
- Place the cursor anywhere in the fourth row (the row with York, George as the salesperson).
- Choose Table > Insert > Rows Above from the menu.
- Add the information shown here to the new row.
| Pillar, James | 5214 | 3247 | 5467 |
Resizing the Columns
You can easily change the size of your column widths. In this exercise, you will select the entire table and adjust all the column widths.- Click anywhere in your table.
- Choose Table > Select > Table from the menu. Your table is selected.
- Choose Table > Table Properties from the menu.
- Choose the Column tab.
- Type 1" in the Preferred Width field. This will cause Microsoft Word to set all the columns to a width of one inch.
- Click OK.
- Place the cursor anywhere in the first column.
- Choose Table > Select > Column from the menu.
- Choose Table > Table Properties from the menu.
- Choose the Column tab.
- Type 1.5 in the Preferred Width field.
- Click OK.
Alternate Method -- Resizing Your Column Widths by Using the Width Indicator
You can resize your column widths by placing the cursor on the line that separates two columns. This causes the width indicator to appear. After the width indicator appears, left-click and drag with the mouse to adjust the column width.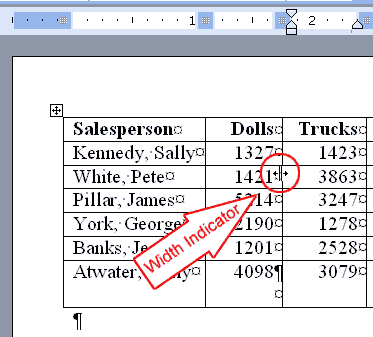
Adding a New Column to a Table
You can add new columns to your table. To add a new column between the Salesperson and Dolls columns:- Place the cursor anywhere in the Dolls column.
- Choose Table > Insert > Columns to the Left from the menu.
- Label the new column Region and add the text shown in the table below.
| Salesperson | Region | Dolls | Trucks | Puzzles |
| Kennedy, Sally | S | 1327 | 1423 | 1193 |
| White, Pete | N | 1421 | 3863 | 2934 |
| Pillar, James | N | 5214 | 3247 | 5467 |
| York, George | S | 2190 | 1278 | 1928 |
| Banks, Jennifer | S | 1201 | 2528 | 1203 |
| Atwater, Kelly | S | 4098 | 3079 | 2067 |
Sorting a Table
With Microsoft Word, it is easy to sort the data in your table. To sort your table data by Region and within Region by Salesperson in ascending order:- Click anywhere on your table.
- Choose Table > Sort from the menu.
- Select Region in the Sort By field.
- Select Text in the Type field (because you are sorting text).
- Select Ascending.
- Select Salesperson in the Then By field.
- Select Text in the Type field (because you are sorting text).
- Select Ascending.
- Select Header Row (because your table has titles across the top of the table).
- Click OK.
| Salesperson | Region | Dolls | Trucks | Puzzles |
| Pillar, James | N | 5214 | 3247 | 5467 |
| White, Pete | N | 1421 | 3863 | 2934 |
| Atwater, Kelly | S | 4098 | 3079 | 2067 |
| Banks, Jennifer | S | 1201 | 2528 | 1203 |
| Kennedy, Sally | S | 1327 | 1423 | 1193 |
| York, George | S | 2190 | 1278 | 1928 |
The Sum Function
You can perform calculations on the numbers in your table. Several functions are available to you. A review of all of the functions is beyond the scope of this tutorial, but the exercise that follows demonstrates the Sum function. In this exercise, you will add a new row to your table, place the word "Total" at the bottom of the Salesperson column, and sum the Dolls, Trucks, and Puzzles columns.- Place your cursor in the cell located on the last row in the last column.
- Press the Tab key to create a new row.
- Type Total in the cell on the bottom row in the Salesperson column.
- Move to the Dolls column.
- Choose Table > Formula from the menu.
- Type =SUM(ABOVE) in the formula field, if it does not automatically appear.
- Select #,##0 in the Number Format field. This selection causes Microsoft Word to separate thousands with a comma.
- Click OK.
- Move to the Trucks column.
- Choose Table > Formula from the menu.
- Type =SUM(ABOVE) in the formula field, if it does not automatically appear.
- Select #,##0 in the Number Format field. This selection causes Microsoft Word to separate thousands with a comma.
- Click OK.
- Move to the Puzzles column.
- Choose Table > Formula from the menu.
- Type =SUM(ABOVE) in the formula field, if it does not automatically appear.
- Select #,##0 in the Number Format field. This selection causes Microsoft Word to separate thousands with a comma.
- Click OK.
Deleting a Column
You can delete columns from your table. To delete the Trucks column:- Place your cursor anywhere in the Trucks column.
- Choose Table > Delete> Columns from the menu.
Deleting a Row
You can delete rows from your table. To delete the York, George row:- Place your cursor anywhere in the York, George row.
- Choose Table > Delete > Rows from the menu.
Recalculate
Unlike a spreadsheet, Microsoft Word does not automatically recalculate every time you make a change to the table. To cause a function to recalculate, you must first move to the cell that contains the function and then press the F9 key. Alternatively, you can move to the cell that contains the function, right-click, and select Update Field from the context menu. Because you deleted a row in the previous exercise, your calculations are now incorrect. To recalculate:- Move to the Dolls/Total cell.
- Press F9.
- Move to the Puzzles/Total cell and right-click.
- Click Update Field.
Merge Cell
Using Microsoft Word, you can merge cells -- turn two or more cells into one cell. In this exercise, you are going to create a new row at the top of your table, merge the cells, and add a title to the table.- Move to the cell located on the first row of the first column of your table (the Salesperson cell).
- Choose Table > Insert > Rows Above from the menu.
- Choose Table > Merge Cells from the menu.
- Type Toy Sales in the new cell.
- Press Ctrl-e to center the title.
Table Headings
If Microsoft Word splits your table with a page break, the table heading will display on the first page but not on subsequent pages. To correct this problem, you can designate rows as headings. Heading rows are repeated on the top of your table at the top of each page. To designate a row as a heading:- Place your cursor on the row.
- Choose Table > Heading Rows Repeat from the menu.
Converting Text to a Table
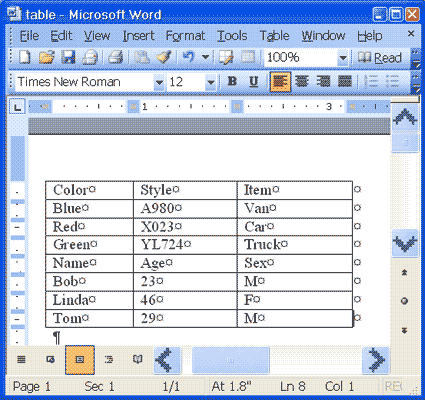
You can convert text to a table; however, a delimiter such as a comma, paragraph marker, or tab must separate columns of text. In the exercise that follows, you will convert comma-delimited text into a table.- Type the following as shown (do not bold).
Color, Style, Item
Blue, A980, Van
Red, X023, Car
Green, YL724, Truck
Name, Age, Sex
Bob, 23, M
Linda, 46, F
Tom, 29, M - Highlight the text.
- Choose Table > Convert > Text to Table from the menu.
- Type 3 in the Number of Columns field.
- Select Auto in the Column Width field.
- Select the Commas radio button in the Separate Text At frame.
- Click OK.
Splitting a Table
With Microsoft Word, splitting a single table into two tables is easy. To separate the table you just created into two tables:- Place your cursor anywhere on the row that reads "Name, Age, Sex."
- Choose Table > Split Table from the menu.
Table AutoFormat
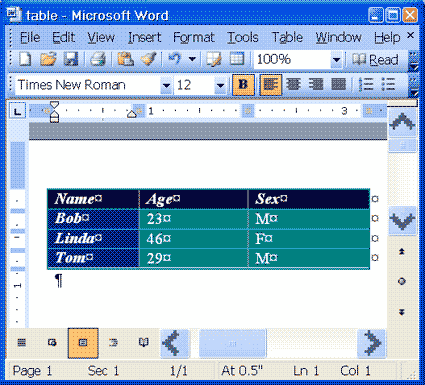
You can use AutoFormats to apply borders, shading, special fonts, and color to your table. Microsoft Word lists all Formats in the Table AutoFormat dialog box. While in the Table AutoFormat dialog box, click a format to see that format displayed in the Preview box. You can customize how the format is applied. Check the features you want in the Formats to Apply and the Apply Special Formats To frames. Microsoft Word comes with a long list of AutoFormats.To apply an AutoFormat to your Name, Age, and Sex table:
- Click anywhere in the table.
- Choose Table > Table AutoFormat from the menu.
- Click Table Colorful 1 in the Table Styles box.
- Select Heading Rows and First Column in the Apply Special Formats To frame. Do not select Last Row and Last Column.
- Click Apply.
Using the Insert Table Toolbar Button to Insert a Table in Your Word Document
There are many ways to insert tables in your Word document. However, the quickest way to create a table from scratch is to use the Insert Table toolbar button.
To insert a table using this method, simply click the Insert Table toolbar button when your cursor is positioned at the place in your document where you would like the table to begin. A grid will pop up allowing you to select how many rows and columns you would like your table to contain. Simply use your mouse to select the number of rows and columns by highlighting the boxes (text at the bottom of the grid will indicate what your selection is). When you have specified the correct number of rows and columns, simply click once, and your table will be inserted.
While this method will create a table with uniform columns and rows, you can still customize your table after it is inserted by right-clicking on the table handle (the double-headed arrow at the top left corner of the table) and using the options on the shortcut menu to make changes. Hint: if you don’t immediately see what you need on the shortcut menu, select Table Properties for more advanced options.
If you’re unfamiliar with the Insert Table button, you can refer to this to help you locate the button on the standard toolbar.
Creating Tables Quickly in Microsoft Word
To insert a table using this method, simply click the Insert Table toolbar button when your cursor is positioned at the place in your document where you would like the table to begin. A grid will pop up allowing you to select how many rows and columns you would like your table to contain. Simply use your mouse to select the number of rows and columns by highlighting the boxes (text at the bottom of the grid will indicate what your selection is). When you have specified the correct number of rows and columns, simply click once, and your table will be inserted.
While this method will create a table with uniform columns and rows, you can still customize your table after it is inserted by right-clicking on the table handle (the double-headed arrow at the top left corner of the table) and using the options on the shortcut menu to make changes. Hint: if you don’t immediately see what you need on the shortcut menu, select Table Properties for more advanced options.
If you’re unfamiliar with the Insert Table button, you can refer to this to help you locate the button on the standard toolbar.
Creating Tables Quickly in Microsoft Word
Word gives you several ways to create a table. You can draw a table or have Word create one from options you specify. There’s also a third way that makes creating a table a cinch.
1. Type a “+” where you want the table to start
2. Tab or space to the point where you want the first column to end
3. Type a “+”
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each column
5. Type a “+” where you want the last column to end
This creates a table with the number of columns you specify. It will only have one row. To add more rows, click outside the table at the end of the first row. Press return. Repeat for each row you would like to add.
The table will function like any table you create in Word. If you need to make alterations to the table layout, access the table properties. (Right-click the 4-headed arrow that appears when you hold you mouse outside the top left corner of the table).
1. Type a “+” where you want the table to start
2. Tab or space to the point where you want the first column to end
3. Type a “+”
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each column
5. Type a “+” where you want the last column to end
This creates a table with the number of columns you specify. It will only have one row. To add more rows, click outside the table at the end of the first row. Press return. Repeat for each row you would like to add.
The table will function like any table you create in Word. If you need to make alterations to the table layout, access the table properties. (Right-click the 4-headed arrow that appears when you hold you mouse outside the top left corner of the table).






 .
.  . Use the sizing handles to adjust position and size of the AutoShape. Right click on the AutoShape - a formatting menu will appear to edit the AutoShape.
. Use the sizing handles to adjust position and size of the AutoShape. Right click on the AutoShape - a formatting menu will appear to edit the AutoShape. .
. 



 . This button is available only when you have text selected.
. This button is available only when you have text selected.

